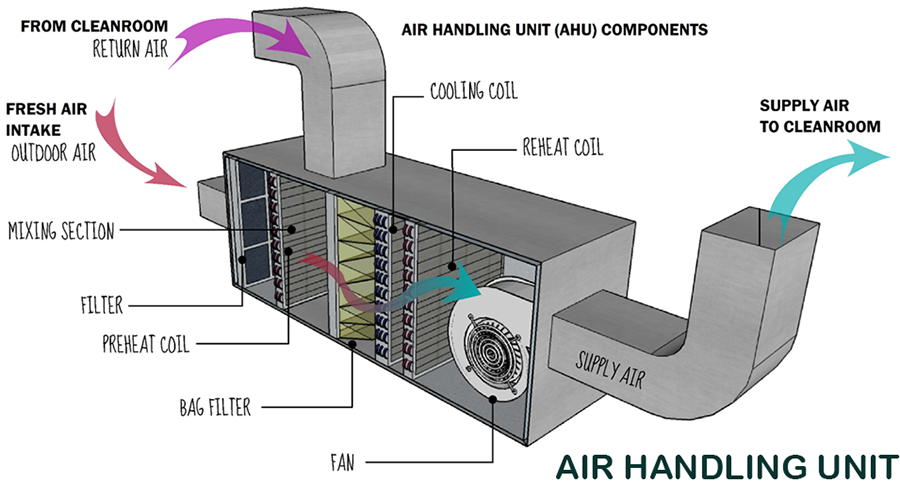
What is an Air Handling Unit AHU?

What is the Air Handling Unit AHU?
Want to learn more aboutAir Handling Unit AHU?Subscribe and follow us on social media.More details on specific FDA expectations for Air Handling Unit AHU can be found in the guidance document below.httpss://www.iso.org/standard/53394.html For a preview, refer to httpss://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:14644:-1:ed-2:v1:en Three (3) options to create a qualification protocol for Air Handling Unit AHUOption 1. You can create a great protocol, using a template.You can download a free sample of a validation template in .pdf format. To see the complete list of the most popular validation templates, click here. In addition, you can request a quotation to buy online a full validation template document in MS Word format that is completely editable, ready to fill, and adapt to your needs. Option 2. We can bring you a formal training on how to create your own validation protocols using our template(s).This option is recommended if you want to learn more about how to build a robust validation protocol. One of our expert(s) will provide online step-by-step training to your team (unlimited assistance) on how to build a reliable validation protocol using a template. You can improve your corporate validation procedures and policies incorporating our template sections. It includes the template, an exam, and a training certificate for each assistant. Request a quote now. Option 3. We can create a customized qualification.One of our expert(s) will create and prepare for you a customized validation protocol with the inputs and specific information of your company. It may include, online support in document creation, execution, or final reporting, Request a quote online. GET IN COMPLIANCE TODAY, CONTACT US (Hablamos Español)STATUTORY AND REGULATORY REQUIREMENTSfor Air Handling Units AHUValidation for drugs (finished pharmaceuticals and components) is a legally enforceable requirement under section 501(a)(2)(B) of the Act (21 U.S.C. 351(a)(2)(B)), which states the following: “… a drug (including a drug contained in a medicated feed) shall be deemed to be adulterated if the methods used in, or the facilities or controls used for, its manufacture, processing, packing, or holding do not conform to or are not operated or administered in conformity with current good manufacturing practice to assure that such drug meets the requirement of the act as to the safety and has the identity and strength, and meets the quality and purity characteristics, which it purports or is represented to possess.” Process validation for drugs (finished pharmaceuticals and components) is a legally enforceable requirement under section 501(a)(2)(B) of the Act (21 U.S.C. 351(a)(2)(B)), which states the following: FDA regulations describing current good manufacturing practice (CGMP) for finished pharmaceuticals are provided in 21 CFR parts 210 and 211. The CGMP regulations require that manufacturing processes be designed and controlled to assure that in-process material and the finished product meet predetermined quality requirements and do so consistently and reliably. Process validation is required, in both general and specific terms, by the CGMP regulations in parts 210 and 211. The foundation for process validation is provided in § 211.100(a), which states that “[t]here shall be written procedures for production and process control designed to assure that the drug products have the identity, strength, quality, and purity they purport or are represented to possess…” (emphasis added). This regulation requires manufacturers to design a process, including operations and controls, which results in a product meeting these attributes. Other CGMP regulations define the various aspects of validation. For example, § 211.110(a), Sampling and testing of in-process materials and drug products, requires that control procedures “. . . be established to monitor the output and to validate the performance of those manufacturing processes that may be responsible for causing variability in the characteristics of in-process material and the drug product” (emphasis added). Under this regulation, even well-designed processes must include in-process control procedures to assure final product quality. In addition, the CGMP regulations regarding sampling set forth a number of requirements for validation: Samples must represent the batch under analysis (§ 211.160(b)(3)); the sampling plan must result in statistical confidence (§ 211.165(c) and (d)); and the batch must meet its predetermined specifications (§ 211.165(a)). In addition to sampling requirements, the CGMP regulations also provide norms for establishing in-process specifications as an aspect of process validation. Section 211.110(b) establishes two principles to follow when establishing in-process specifications. The first principle is that “. . . in-process specifications for such characteristics [of in-process material and the drug product] shall be consistent with drug product final specifications . . . .” Accordingly, in-process material should be controlled to assure that the final drug product will meet its quality requirements. The second principle in this regulation further requires that in-process specifications “. . . shall be derived from previous acceptable process average and process variability estimates where possible and determined by the application of suitable statistical procedures where appropriate.” This requirement, in part, establishes the need for manufacturers to analyze process performance and control batch-to-batch variability. The CGMP regulations also describe and define activities connected with process design, development, and maintenance. Section 211.180(e) requires that information and data about product quality and manufacturing experience be periodically reviewed to determine whether any changes to the established process are warranted. Ongoing feedback about product quality and process performance is an essential feature of process maintenance. In addition, the CGMP regulations require that facilities in which drugs are manufactured be of suitable size, construction, and location to facilitate proper operations (§ 211.42). Equipment must be of appropriate design, adequate size, and suitably located to facilitate operations for its intended use (§ 211.63). Automated, mechanical, and electronic equipment must be calibrated, inspected, or checked according to a written program designed to assure proper performance (§ 211.68). Referenceshttpss://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=225.1 httpss://www.fda.gov/media/94074/download httpss://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=225.1 httpss://ispe.org/publications/guidance-documents/gamp-5 httpss://www.fda.gov/media/94074/download httpss://www.fda.gov/media/94074/download httpss://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=225.1 httpss://ispe.org/publications/guidance-documents/gamp-5 Related topics and resources:Validation Plan, Installation Qualification, Operational Qualification, Performance Qualifications, Component Qualification, Traceability Matrix, Ppk, Control Charts, Cpk, User Requirements, Functional Requirement Specifications, GAMP5, risk assessment |

Ramon Cayuela, MS, BS, Chemical Engineering
CIQA President and CEO.
I've been working in validation engineering since 1992 with many multinational pharmaceutical companies. I love sharing my passion and knowledge with others. If you have any questions about anything (or just have general questions). I will be more than happy to assist you. You can count on the BEST customer service on CIQA. I go to great lengths to make sure my clients are 100% satisfied with their purchases and check emails/messages consistently throughout the day. You can rest assured that everything being sold here is as-described or your money back. I look forward to working with you!
Related Articles
Subscribe to get validation
news and free tips by email.
Need Additional Help?